We can simplistically define organizational structures as a design by the organization's senior management that clarifies the division of managerial positions. It always starts at the highest level and progresses to the lowest level. This sequence explains the process of receiving decisions from senior management, guiding them through all relevant departments, and elucidating effective communication methods among departments. There are many types of organizational structures in institutions, depending on the differences in activities, responsibilities, and tasks between each institution and another, the size of the institution, the nature of its work, and the number of employees within it, as we will know in the next few lines.
Characteristics of good organizational structures
Without a doubt, the primary purpose of organizational structures is to assist senior management in achieving their stated goals and fostering effective, flexible, and rapid communication among specialized departments. We can identify several criteria to evaluate the effectiveness of this organizational structure, which are as follows:
- Making the most of specialization: One of the important characteristics of organizational structures is that the organization benefits from the individual’s specialization. Establishing a specialized unit for each task within the structure achieves this. This results in a reduction in costs, a quicker completion of work, and an increase in employee agreement and flexibility.
- Complete coordination between the organization's work: This helps to avoid duplication in issuing decisions and in the work of all units of the organizational structure with the greatest possible efficiency, not duplicating work, as well as coordination of all efforts within the facility
- Highlighting important and influential activities: The nature of departmental work within organizational structures varies depending on priorities. In the organization's work, there are basic departments and secondary departments. The organizational structure is useful in placing the basic departments in a larger position appropriate to their importance and specialization.
- The principle of automatic self-monitoring is achieved, one of the most important characteristics of the organizational structure within the institution, so that each department monitors the most important daily activities through the head of this department and does not require the presence of an observer from the top of the organizational structure, such as the general manager or the chairman of the board of directors, for example.
Types of organizational structures
There are many types of organizational structures, which vary according to the nature of the activity for which they are designed. In the following lines, we will review the most important types of organizational structures, as follows:
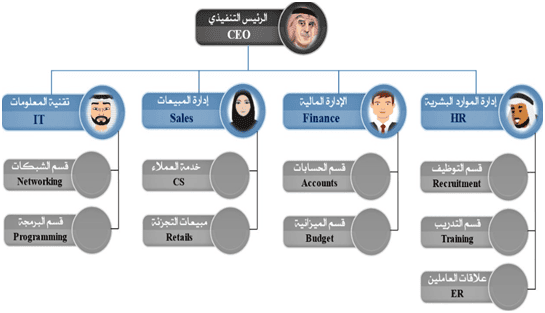
1. Functional organizational structure:
It is one of the most famous organizational structures in institutions, and it places people by job. Departments like financial management, marketing management, and purchasing management branch out from the organization's head, and departments within departments branch out from it.
The functional organizational structure features
- It helps employees carry out tasks because there are clear lines of authority and administrative decision sequences.
- Strengthening self-monitoring in each department ensures that the basic work activity is carried out accurately and efficiently.
Disadvantages of functional organizational structure
- The difficulty of departments communicating with each other, affects the integration of work in some activities.
- The functional organizational structure does not create a spirit of innovation and creativity, and this creates a kind of dependency in the sense that each department depends on the other to achieve the goal of the work.
Functional organizational structure model
2: Matrix organizational structure
A type of organizational structure that has become popular at the present time. The formation of the matrix organizational structure is summarized in the presence of more than one manager to whom daily reports are submitted. Under the CEO of the project, there are various departments, which are divided into projects, and each project has an integrated team of specialized employees.
Features of the matrix organizational structure
- Forming an integrated work team that helps employees develop creativity and innovation skills.
- It gives each employee extensive experience and knowledge of different departments and divisions.
- Solve problems in more effective ways and give more flexibility within the organization.
Disadvantages of the matrix organizational structure
- Some ambiguity appears among employees, such that they sometimes do not know to which manager reports will be submitted, and this leads to confusion between responsibilities and job tasks.
- It is difficult to evaluate employee performance due to the large number of projects and sometimes overlapping responsibilities.
Matrix organizational structure model

3. Network organizational structure
Companies that rely on external sources or have agencies in various countries, and seek to oversee the operations of branches located far away, can utilize this structure. In this design, managers control their internal and external relationships.
Features of the network organizational structure
- This type reduces costs significantly because it relies on external labor, such as the person who takes the agency from the company and is the one who appoints employees.
- It helps the company respond quickly to market changes and provides complete flexibility in changing work mechanisms.
Disadvantages of the network organizational structure
- Increased risk rates as the company deals with agents only.
- The company deals with a large number of employees, which leads to confusion in decision-making.
- This organizational structure lacks direct oversight of employees.
Network organizational structure model

4: Hierarchical organizational structure
The hierarchical organizational structure consists of the top of the pyramid, which is the general manager or chairman of the board of directors, and below him are the project and department managers. After that, each manager has a group of employees under him in a hierarchical hierarchy from the oldest to the youngest.
Features of the hierarchical organizational structure
- Passing administrative decisions quickly, which contributes to maintaining working times within the organization.
- It allows each manager to fully concentrate on his specialty and not be distracted by many departments and divisions.
- It also allows employees to see the path to higher management positions and try to reach them.
Disadvantages of hierarchical organizational structure
- Disrupting direct communication between employees, leading to the feeling that they are working on isolated islands.
- It is possible to find within the hierarchical organizational structure jobs that have no work and are considered a burden on the organization, which costs the company huge amounts of money in vain.
Hierarchical organizational structure model

5: Flat organizational structure
It is considered one of the simplest types of organizational structures, as there are no departments in this structure between senior departments and employees, so the employee communicates directly with the higher administrative levels. This organizational chart is suitable for start-up companies and is simple in structure. This chart also allows independence and self-reliance, a lack of fear of direct managers, and rapid communication with all elements and departments of the company.
Advantages of a flat organizational structure
- Involving the largest number of employees in support and decision-making processes contributes to establishing a strong relationship between employees and the facility.
- Raising levels of effective communication between employees and each other and between employees and senior management.
- Reducing costs by having fewer employees.
Disadvantages of a flat organizational structure
- Because there are no direct superiors for employees, it is possible for superiors to be busy solving small problems and abandon their primary work.
- Employees feel lax at work, and indifference seeps in due to the lack of direct supervision over them and the absence of direct superiors.
A flat organizational structure model
6: Divisional organizational structure
This organization is characterized by the presence of different sectors below the Chairman of the Board of Directors, and each sector includes a group of departments, and each department includes a group of supervisors and then employees. This plan is suitable for industrial institutions that have many production lines.
Features of the divisional organizational structure
- Due to the diversity of the factory’s geographical areas, it contributes to the organization's spread and knowledge.
- All reports are issued accurately and detailed to the departments and, from there, to the company's CEO.
Disadvantages of a divisional organizational structure
- Overlapping specializations in different sectors and a feeling of confusion in carrying out the required tasks.
- There is difficulty determining the specific needs of each sector, especially if it is in a different region.
divisional organizational structure model

divisional organizational structure model
Factors affecting the choice of organizational structures
We must take into account a certain number of factors that directly affect the design of organizational structures in different institutions and mention them as follows:
- Size of the establishment: The size of the establishment greatly affects the choice of organizational structures. If the organization is small, simple structures in composition, such as the functional structure, are suitable. However, if it is large, it will need more organization, such as a network or matrix organization, according to the nature of the activity.
- The organization's strategy: If the organization wants continuous development, it chooses flexible and sophisticated organizational structures.
- The geographical location of the facility: It greatly affects the choice of organizational structure. If the company has branches in different regions, the pyramid scheme or the closest organizational structure is to it.
Conclusion
Here, we have completed a detailed presentation of the most important types of organizational structures in institutions, whether for commercial or industrial purposes. We have also mentioned the distinctive characteristics of these structures and the factors influencing the selection of the appropriate organizational structure. We hope that we have succeeded in presenting this.
Join our inspiring community! Subscribe to our LinkedIn page and Twitter to be the first to know about the latest articles and updates. An opportunity for learning and development in the world of accounting and finance. Don’t miss out, join us today!


















.png?width=206&height=208&name=Mask%20group%20(1).png)
